Geminid Meteor Shower Peaks Tonight How to Watch

Geminid Meteor Shower Peaks Tonight: When and How to Watch the Sky Show
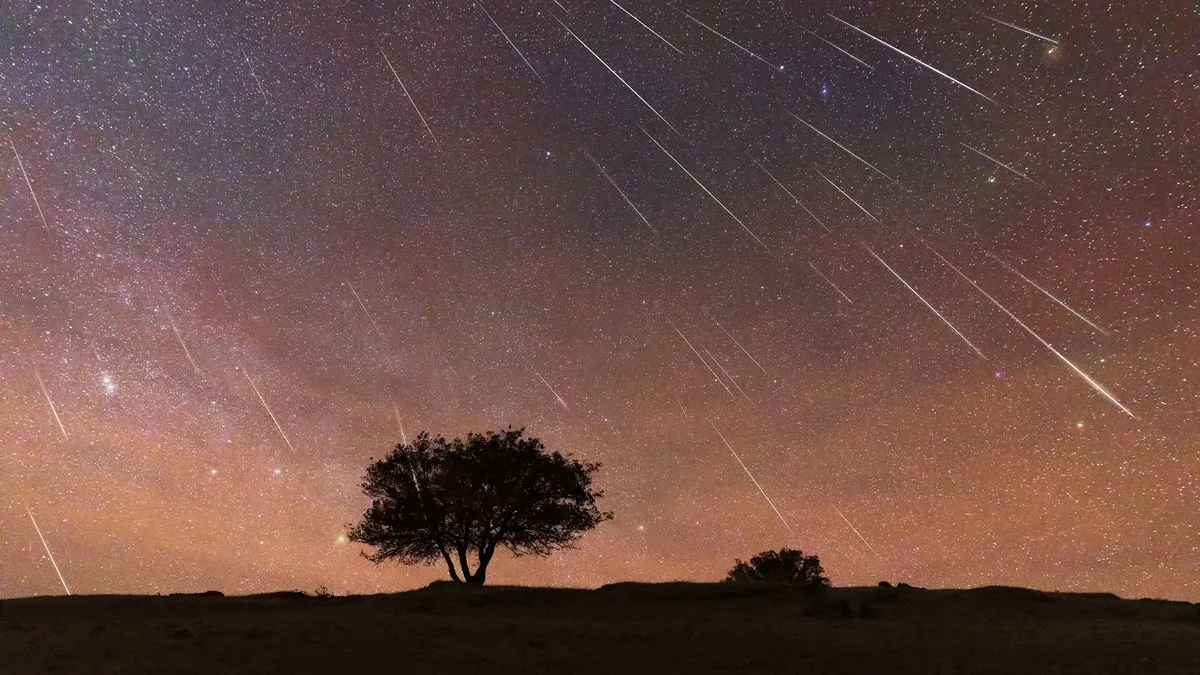
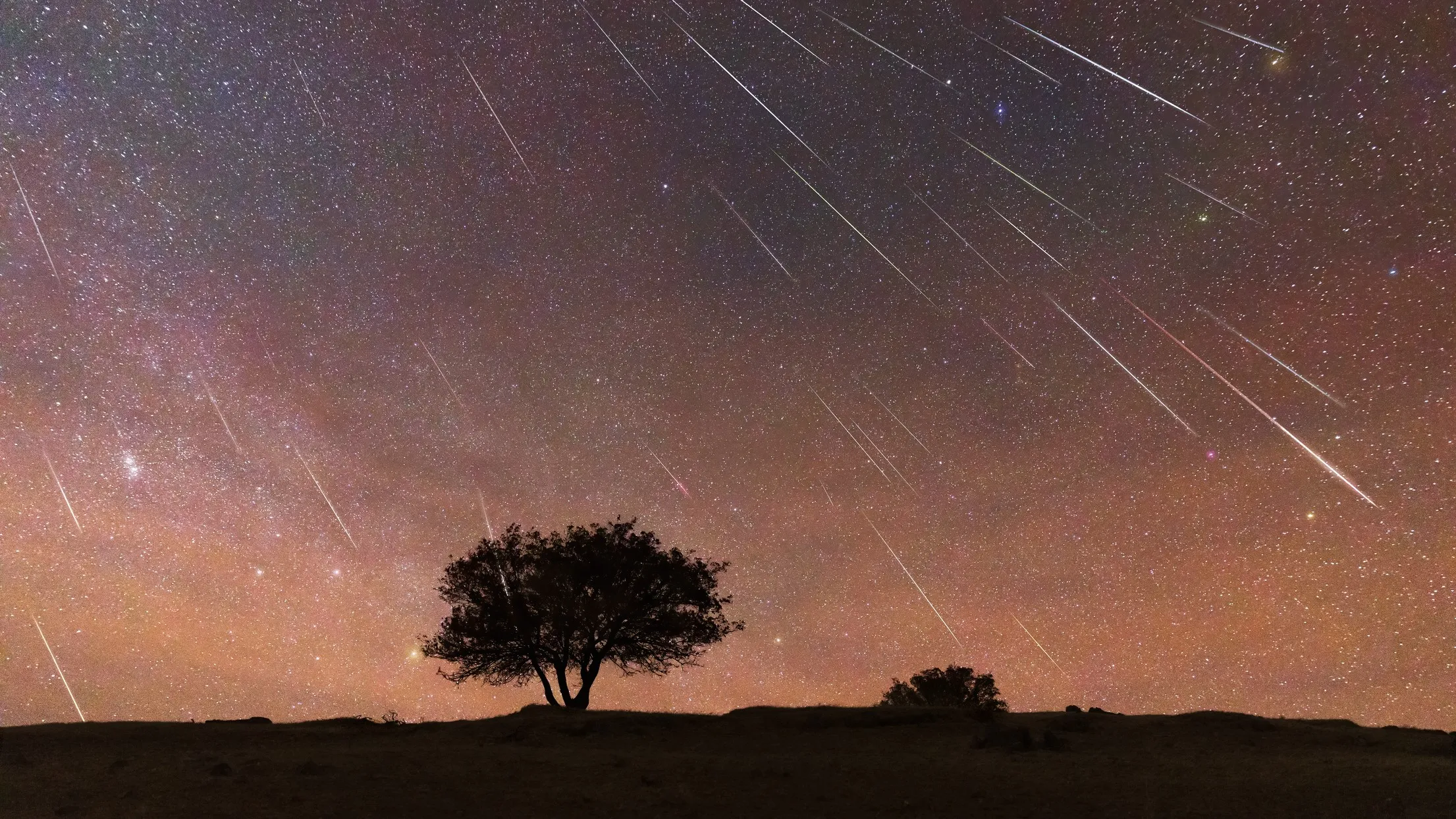
The Geminid meteor shower is widely regarded as one of the most spectacular and dependable annual celestial events visible from Earth. Skywatchers across the globe are preparing for its peak, which will occur overnight between Saturday and Sunday, December 13 and 14. Under favorable conditions, observers may witness up to 100 shooting stars per hour, making this meteor shower one of the most active displays of the year.
Adding to the visual appeal, the bright planet Jupiter will be clearly visible near the radiant constellation during the peak hours. This rare combination of high meteor activity and planetary brilliance enhances the overall stargazing experience, drawing both amateur skywatchers and seasoned astronomers outdoors.

What Is a Shooting Star?
A shooting star is not a star at all, but a meteor that enters Earth's atmosphere at an immense speed of approximately 22 miles per second. As the small particle collides with atmospheric gases, friction causes it to heat rapidly and glow, producing a brief streak of light that is visible from the ground for a fraction of a second.
Geminid meteors are especially admired for their striking colors. While many appear greenish due to ionized nickel content, others may flash bluish or yellowish hues depending on their chemical composition and interaction with the atmosphere. These vibrant colors make the Geminids stand out from other meteor showers.

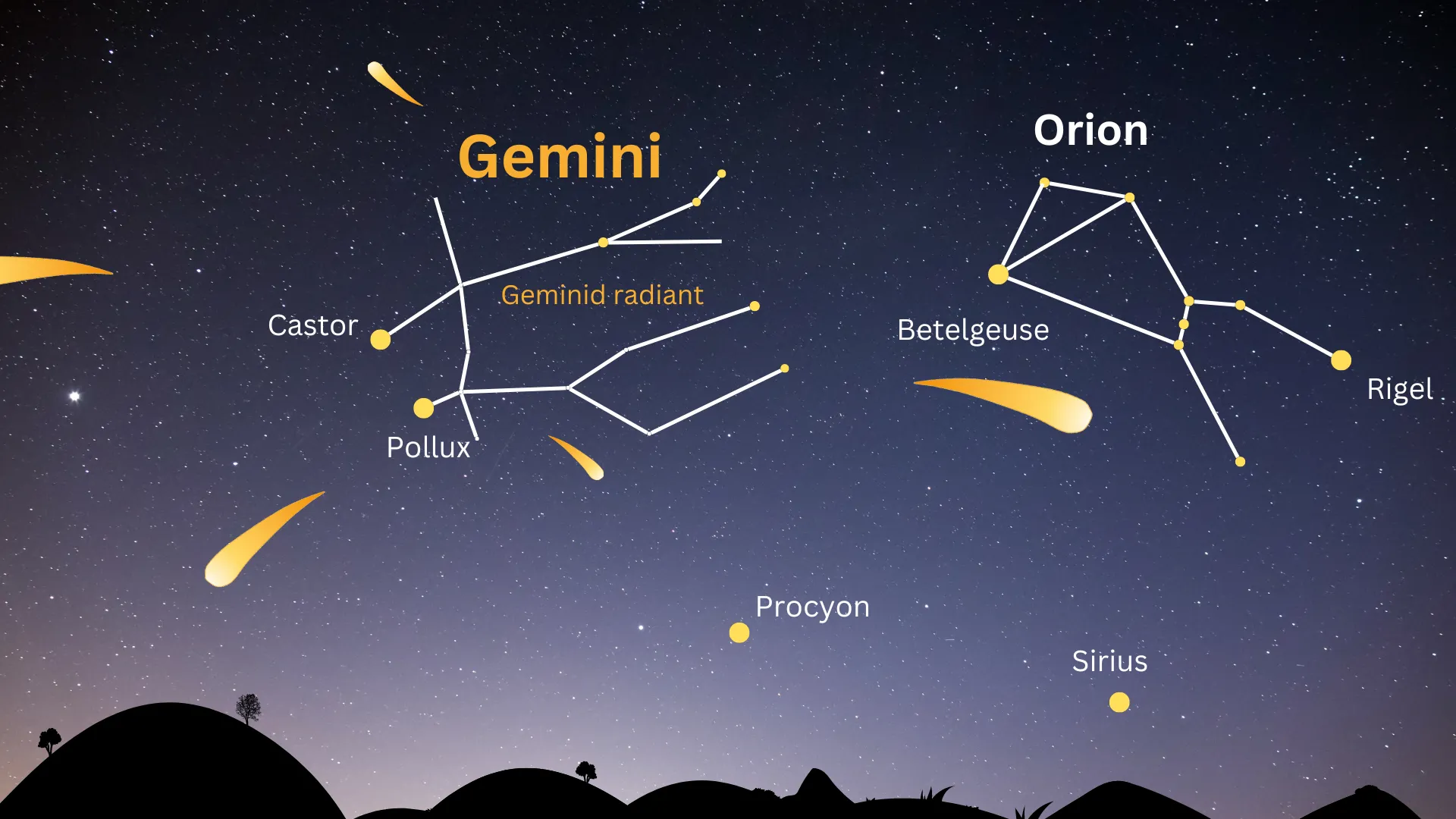
Geminid Meteor Shower Explained
First observed in 1862, the Geminid meteor shower is unique among major meteor displays because it originates from an asteroid rather than a comet. The parent body, known as 3200 Phaethon, sheds rocky debris that Earth encounters annually as it travels along its orbital path.
Over the years, the Geminids have gained a reputation for strength and reliability. While theoretical peak rates can reach as high as 150 meteors per hour, real-world observations are often lower due to light pollution, atmospheric conditions, and the limitations of human vision. Even so, the Geminids remain one of the most impressive meteor showers visible each year.
Best Time to Watch the Geminids
The ideal time to observe the Geminid meteor shower is when its radiant point, the constellation Gemini, is positioned high in the night sky. This typically occurs between 10 p.m. and 2 a.m. local time, when darkness is deepest and meteor visibility is greatest.
During the 2025 peak, a 25 percent illuminated crescent moon will rise around 2 a.m. While moonlight can slightly reduce meteor visibility, the relatively low brightness of the moon ensures that viewing conditions remain favorable for much of the night.

Three Best Observation Periods
The Geminid meteor shower unfolds gradually through the night, with meteor activity increasing as the hours pass. While shooting stars can appear at any time after sunset, certain periods offer noticeably better visibility based on the position of the constellation Gemini and the darkness of the sky. Breaking the night into three observation windows helps skywatchers plan the best time to step outside and maximize their chances of witnessing the most meteors.
Early Evening: Earthgrazers
Shortly after darkness sets in, meteor rates are relatively low. However, the meteors that do appear during this time are often Earthgrazers, which skim the upper atmosphere at shallow angles. These meteors tend to last longer and appear brighter, creating dramatic streaks across the sky.
Around 10 p.m.
By around 10 p.m., meteor activity noticeably increases. Observers may see approximately 30 Geminid meteors per hour, especially when facing east. This period offers a good balance between comfort and visibility for those who prefer earlier viewing.
Midnight to 4 a.m.
The highest activity occurs between midnight and the early morning hours, peaking around 2 a.m. During this window, observers under dark rural skies may see up to 60 meteors per hour. Activity gradually decreases afterward as the moon rises higher and Gemini shifts toward the western sky.
Tips for Watching the Geminids
Watching the Geminid meteor shower requires no special equipment. The naked eye is the most effective tool, allowing viewers to take in a wide portion of the sky. Allowing at least 20 minutes for eyes to adjust to the darkness can significantly improve visibility.
Staying warm, hydrated, and taking breaks during extended viewing sessions can improve comfort and endurance. Since meteors appear suddenly and vanish quickly, patience is essential for a rewarding experience.
Astrological Significance of Shooting Stars
In Astrology, shooting stars are often seen as powerful symbols of sudden change, hope, and divine timing. Many believe that witnessing a meteor streak across the sky represents the universe opening a brief window for intentions and fresh beginnings. The Geminid meteor shower, radiating from the constellation Gemini, is thought to amplify themes of communication, clarity, and new ideas. For astrology followers, this celestial event is considered an ideal moment to pause, reflect, and silently set personal intentions while observing the night sky.
Best Viewing Conditions
Clear skies and minimal light pollution are crucial for optimal meteor viewing. Urban glare can significantly reduce visibility, so traveling to darker locations away from city lights can greatly enhance the experience. Weather conditions should always be checked before heading out to ensure unobstructed views.
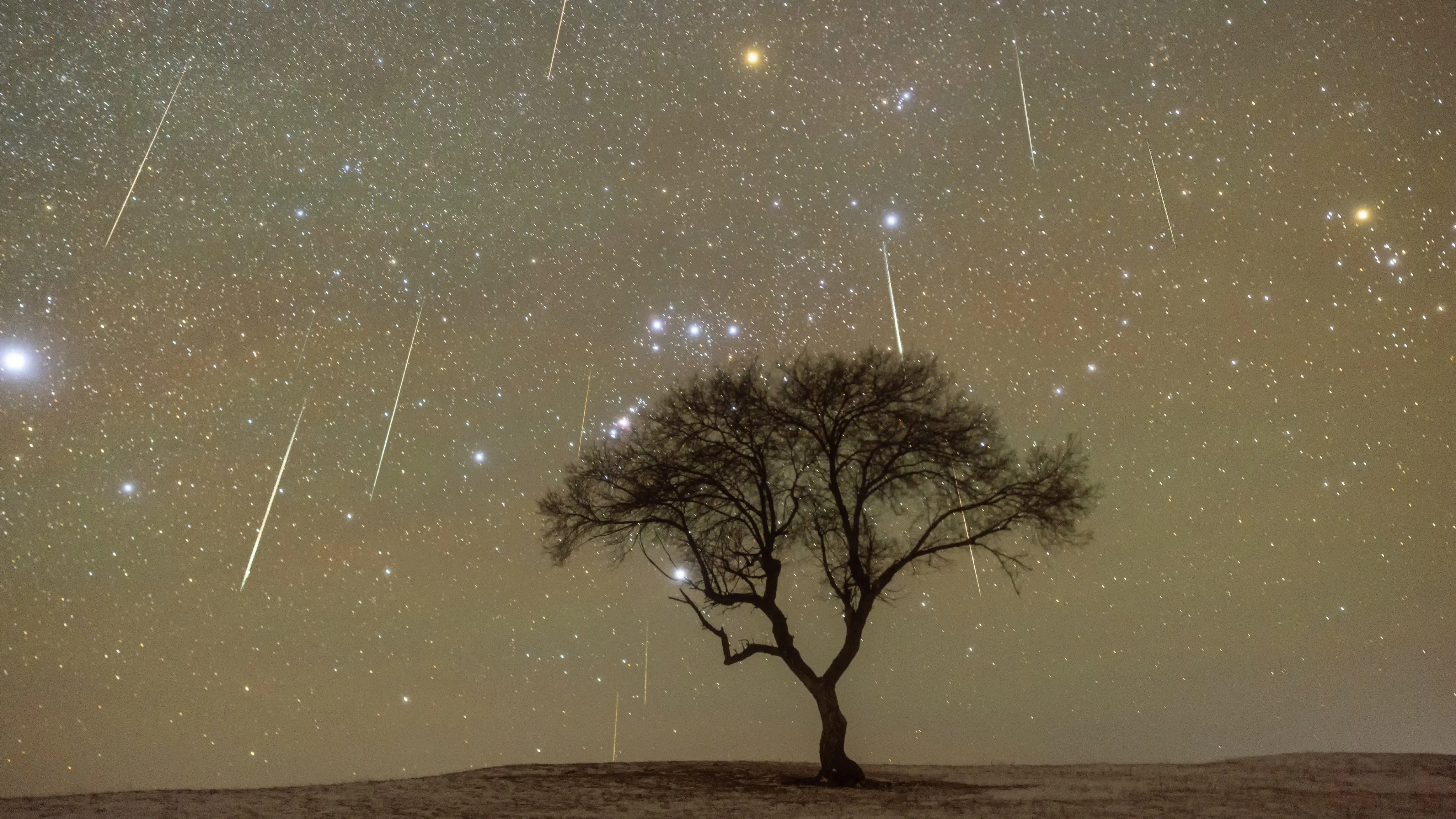

How to Photograph the Geminids
Photographing meteors is challenging with smartphones due to their speed, but DSLR or mirrorless cameras with manual controls are well-suited for the task. Using a tripod, wide-angle lens, high ISO settings, and long exposure times increases the likelihood of capturing meteors.
Continuous shooting over one to two hours improves success rates. Afterward, images can be reviewed individually or combined into composite photographs that showcase multiple meteors in a single frame.
What's Next in the Night Sky
If cloudy weather disrupts Geminid viewing, another opportunity arrives later in December with the Ursid meteor shower. Peaking on December 21 near the winter solstice, the Ursids offer a smaller but still noteworthy display for dedicated skywatchers.
Comment / Reply From
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!









