Should You Take Supplements On An Empty Stomach? Comprehensive Guide
Should You Take Supplements On An Empty Stomach? A Comprehensive Guide
Health supplements have become an essential part of many wellness routines worldwide. From boosting immunity to filling nutritional gaps, supplements play a key role in supporting our overall health. However, a frequent question many have is whether it’s safe or effective to take supplements on an empty stomach. The answer depends on multiple factors such as the type of supplement, your personal digestive health, and your body’s response.
The Role of Food in Supplement Absorption
Food significantly impacts how our bodies absorb and utilize nutrients from supplements. Some vitamins and minerals require the presence of dietary fats or certain digestive enzymes to be absorbed efficiently. Others can cause stomach irritation if consumed without food. By understanding these relationships, you can optimize supplement efficacy and avoid discomfort.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K)
Fat-soluble vitamins dissolve in fats and require dietary fat to absorb properly. Taking these vitamins with meals containing healthy fats such as olive oil, nuts, cheese, or avocado can enhance their absorption. For example, pairing vitamin D supplements with breakfast including eggs or cheese maximizes their benefit.
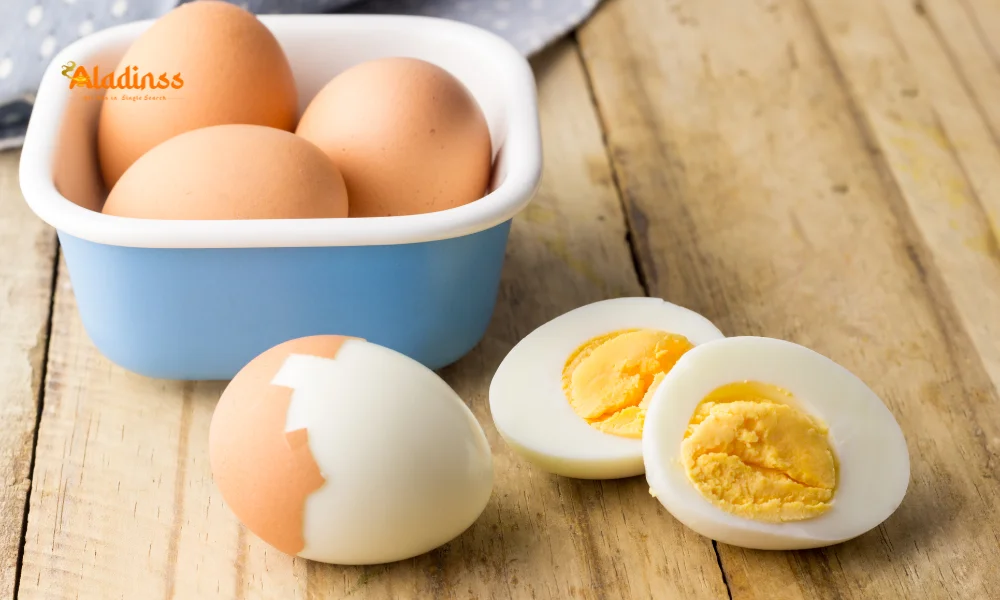
Calcium and Iron
Calcium absorption is more efficient when taken in smaller doses (500–600 mg) with food. Taking it on an empty stomach can reduce its bioavailability. Iron is somewhat unique; it is best absorbed on an empty stomach but can cause nausea or constipation for sensitive individuals. Pairing iron with vitamin C-rich foods (like orange juice or bell peppers) improves absorption, but if stomach upset occurs, taking iron with meals is advisable.
Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that improve gut health. They survive better when consumed with food, which protects them from stomach acid and increases the number of bacteria reaching the intestines.
Herbal Supplements (e.g., Turmeric)
Herbal supplements like turmeric contain active compounds such as curcumin that are fat-soluble. Taking turmeric with a source of fat and black pepper (piperine) helps improve its absorption significantly.
Supplements You Can Safely Take on an Empty Stomach
Water-Soluble Vitamins (B-Complex, Vitamin C)
Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and generally do not require food for absorption. However, high doses might cause stomach upset, so if you experience discomfort, it’s better to take them with a light snack.
Magnesium
Magnesium supplements can be taken without food, but large doses may cause diarrhea or abdominal cramps. If you notice these symptoms, try taking magnesium with meals to improve tolerance.
Certain Herbal Supplements (e.g., Ginger)
Ginger is known for its natural anti-inflammatory and stomach-soothing properties, making it suitable for morning consumption on an empty stomach.
Key Considerations for Individuals
- Stomach Sensitivity: Conditions like acid reflux, gastritis, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may make it necessary to avoid taking supplements on an empty stomach to prevent irritation.
- Age and Digestive Health: Older adults or people with compromised digestion may benefit from taking supplements with food to enhance absorption and reduce discomfort.
- Medication Interactions: Some supplements can interact with medications (e.g., vitamin K and blood thinners). It’s essential to consult your healthcare provider before starting supplements.
Practical Tips for Safe Supplement Use
- Follow Label Instructions: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions on supplement packaging, as many specify whether to take with or without food.
- Start with Low Doses: Introduce new supplements gradually with meals to monitor tolerance and reduce side effects.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to signs like nausea, cramps, or diarrhea. If these occur, adjust timing or dosage accordingly.
- Consult a Professional: For personalized advice based on your health conditions and goals, speak with a doctor, dietitian, or pharmacist.
Conclusion: Personalize Your Supplement Routine for Best Results
Taking supplements on an empty stomach is not universally beneficial or harmful—it depends on the supplement type and your individual needs. Fat-soluble vitamins and some minerals require food for optimal absorption, while water-soluble vitamins and certain herbal supplements may be taken without food. Being mindful of your body's reactions and following expert advice can help you gain the maximum benefit from your supplements while avoiding unpleasant side effects.
Ultimately, always prioritize your unique health profile and consult healthcare professionals for guidance. Proper timing and method of supplement intake can enhance wellness, making your health journey safer and more effective.
Comment / Reply From
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!






