Baldness Symptoms in Men vs. Women: How to Recognize and Prevent Hair Loss
Baldness Symptoms in Men vs. Women: How to Recognize and Prevent Hair Loss
Hair loss is a widespread issue that affects millions of people worldwide, but the way it manifests in men and women differs significantly due to hormonal, genetic, and environmental factors. Understanding these differences is crucial for recognizing the early signs of baldness and taking proactive steps to prevent or manage it. While both genders experience hair thinning, the patterns, causes, and emotional impacts vary, requiring tailored approaches to treatment. This article explores how baldness symptoms differ between men and women, highlights key indicators to watch for, and offers practical prevention strategies to maintain healthy hair.
Understanding Baldness: Why It Differs Between Men and Women
Baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is the most common form of hair loss, affecting both men and women but presenting in distinct ways. In men, baldness often follows a predictable pattern, while in women, it tends to be more diffuse and less severe. These differences stem from hormonal influences, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle factors. Recognizing the unique symptoms of hair loss in each gender can reduce stress and guide individuals toward effective treatments. Early intervention is key, as timely action can slow hair loss and, in some cases, promote regrowth.
For men, baldness is often linked to aging and masculinity, leading to societal pressures that can exacerbate emotional distress. Women, on the other hand, may face heightened appearance-related anxiety due to cultural expectations around hair and beauty. By understanding the nuances of male and female pattern baldness, individuals can make informed decisions about prevention and treatment, improving both their physical and emotional well-being.
Where Does Hair Loss Start?
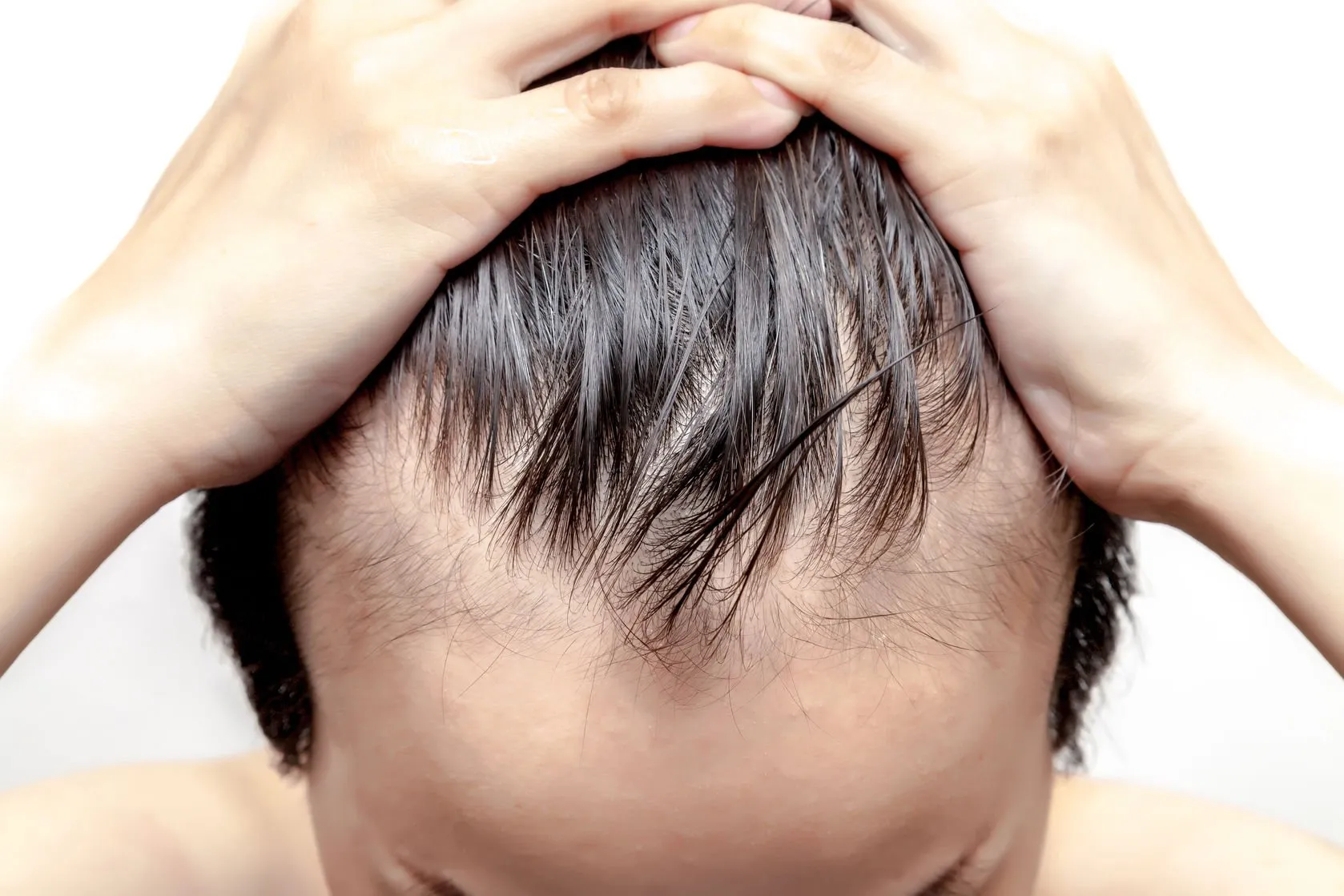

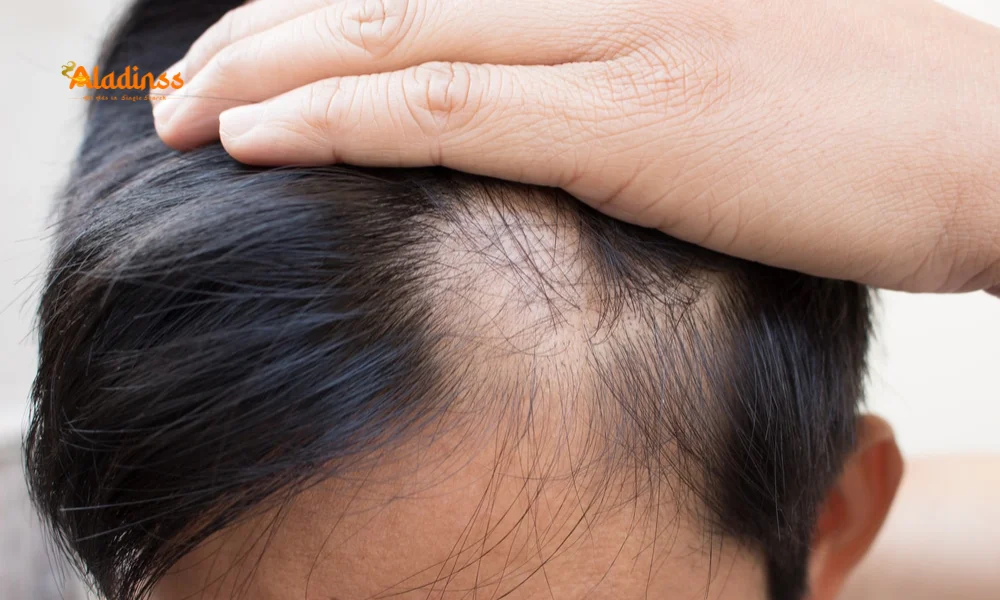
In men, hair loss typically begins at the crown and frontal hairline, progressing to form a characteristic “M” shape as the hairline recedes. Over time, the thinning spreads, often resulting in partial or complete baldness at the top of the head while hair on the sides and back remains intact. This pattern, known as male pattern baldness, is driven by genetic and hormonal factors that cause hair follicles to shrink and produce finer, shorter hairs.
In contrast, women experience diffuse hair thinning across the entire scalp, particularly at the crown. Unlike men, women rarely develop completely bald areas; instead, their hair becomes noticeably thinner, with the scalp becoming more visible. This diffuse pattern, known as female pattern hair loss, is often linked to hormonal changes and can be exacerbated by stress, pregnancy, or menopause. Recognizing these distinct patterns is the first step in identifying baldness and seeking appropriate treatment.
When Does Hair Loss Start?
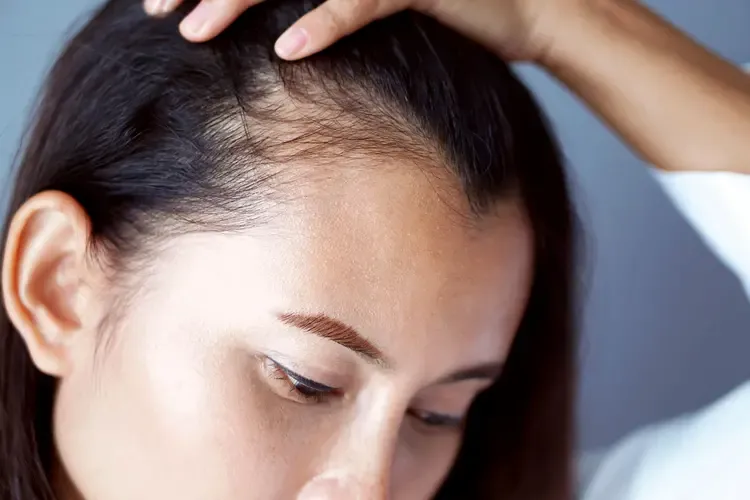

The onset of hair loss varies significantly between men and women. For men, significant thinning or baldness often begins in their 20s or 30s, with the majority experiencing some degree of hair loss by their 50s or 60s. Male pattern baldness tends to progress steadily, with early signs like a receding hairline becoming more pronounced over time if left untreated.
Women, however, typically notice hair loss later in life, often after the age of 40. Key triggers include menopause, childbirth, or other hormonal shifts that reduce estrogen levels, which normally protect hair follicles. While men may see rapid hair loss in their youth, women’s hair thinning is more gradual, making early detection and intervention critical for managing progression.
Effect of Hormones on Hair Loss
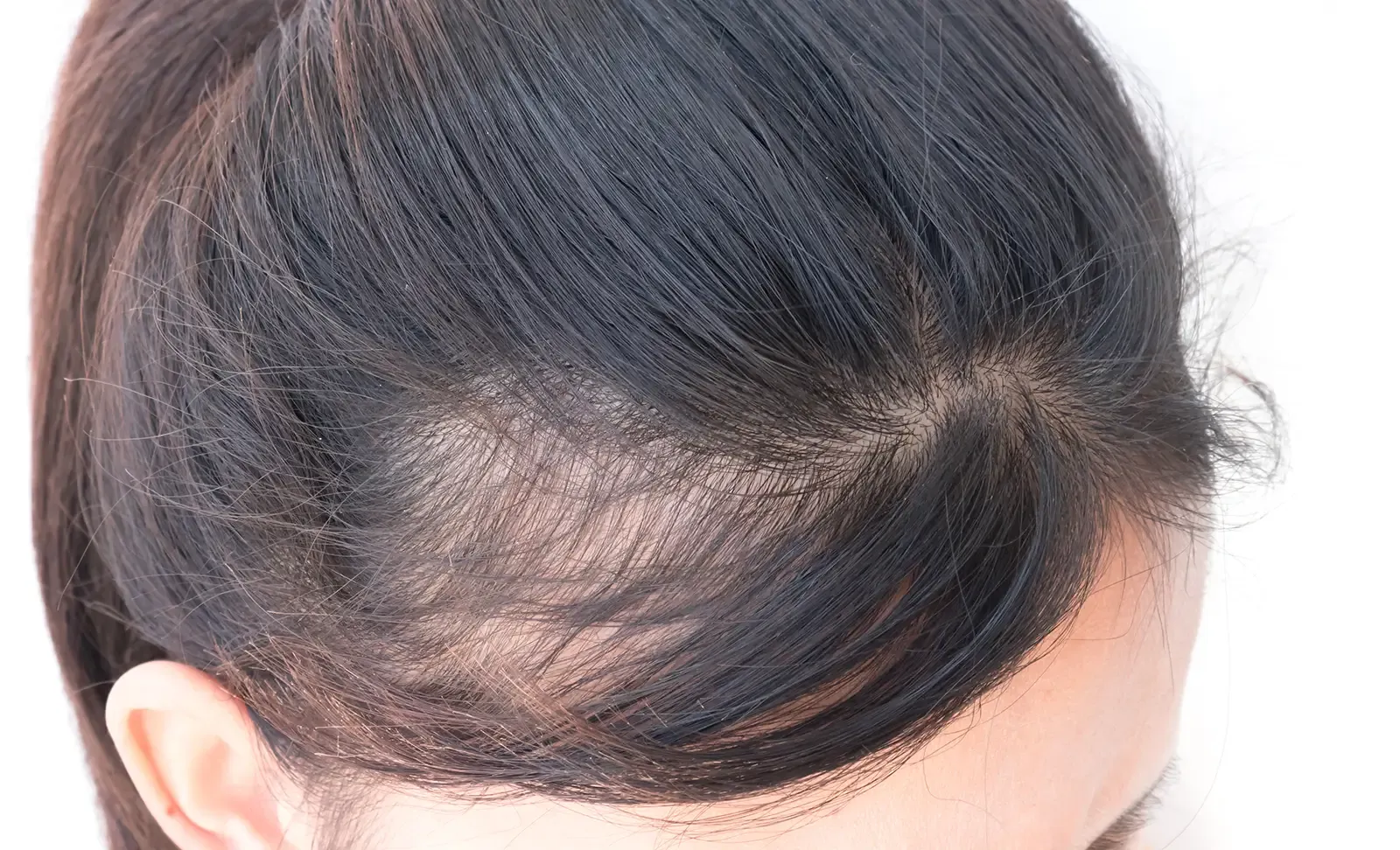
Hormones play a central role in hair loss for both genders, but their impact differs. In men, testosterone and its derivative, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are the primary culprits. DHT binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing hair. This process is why male pattern baldness is often more severe and localized to specific areas like the crown and hairline.
In women, estrogen acts as a protective hormone, supporting hair growth and follicle health. When estrogen levels drop—during menopause, pregnancy, or other hormonal imbalances—hair follicles weaken, leading to increased shedding and thinning. Women are less affected by DHT, which explains why their hair loss is typically less severe and more diffuse. Understanding these hormonal influences can guide targeted treatments, such as hormone therapy or DHT blockers, to manage hair loss effectively.
Rate of Progression of Baldness
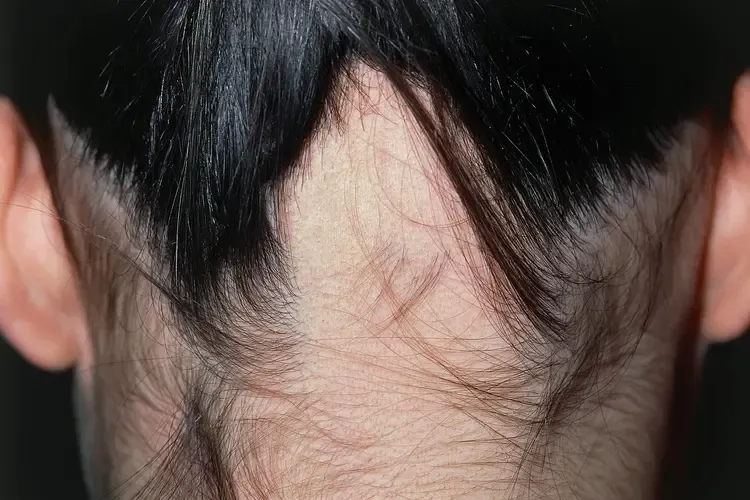
The speed at which hair loss progresses varies significantly between men and women. In men, baldness can advance rapidly, with receding hairlines and bald spots expanding quickly if no intervention occurs. This rapid progression is driven by the aggressive action of DHT on hair follicles, leading to noticeable bald patches within a few years.
Women, however, experience a slower, more gradual thinning process. This allows for earlier intervention, which can significantly slow or even halt hair loss with the right treatments. Regular scalp monitoring and early consultation with a dermatologist can help women manage hair thinning before it becomes more pronounced, offering a window of opportunity to preserve hair density.
Emotional Impact of Hair Loss
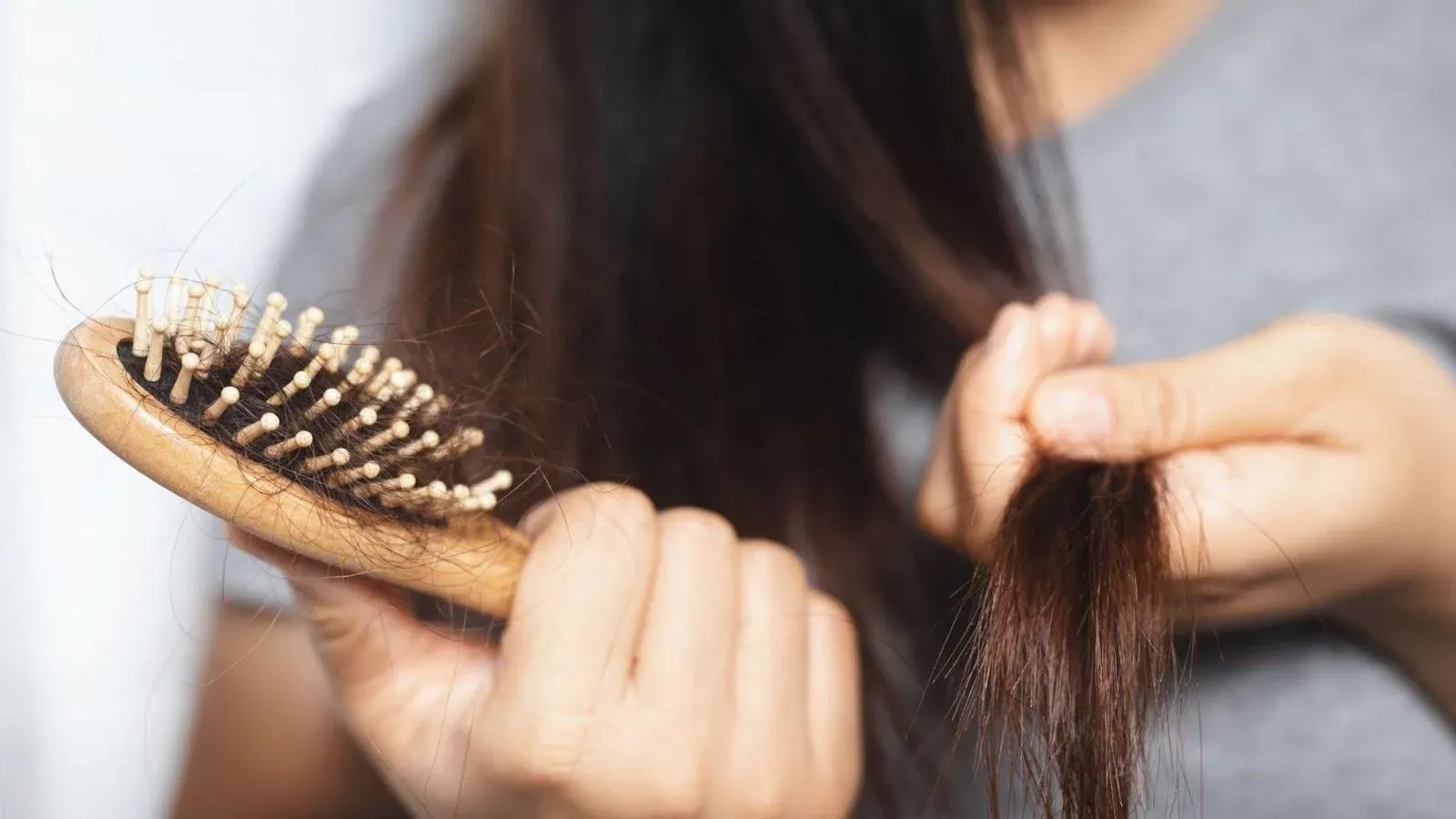

Hair loss can have a profound emotional impact on both men and women, though the experiences differ. For men, baldness is often associated with aging or a perceived loss of vitality, leading to feelings of depression, embarrassment, or reduced self-esteem. Societal perceptions of baldness as a sign of weakness can exacerbate these feelings, prompting many men to seek treatments or conceal their hair loss.
Women face unique challenges, as hair is closely tied to societal standards of beauty. Thinning hair can lead to heightened anxiety, social pressure, and a reluctance to seek help due to stigma. Although complete baldness is rare in women, the emotional toll of diffuse thinning can be significant, often leading to isolation or avoidance of social situations. Addressing the emotional impact through support groups or counseling can be as important as medical treatments.
Prevention and Treatment Options
Preventing and managing hair loss requires a tailored approach based on gender and the underlying causes. For men, treatments like minoxidil (a topical solution) and finasteride (a DHT blocker) can slow hair loss and promote regrowth in some cases. Early intervention is critical, as these treatments are most effective in the early stages of male pattern baldness. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, eating a nutrient-rich diet, and avoiding harsh hair products, can also support hair health.
For women, treatments may include minoxidil, hormonal therapies to address estrogen imbalances, or supplements like biotin and iron to support hair growth. Addressing underlying conditions, such as thyroid disorders or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can also help manage hair loss. Scalp massages, gentle hair care routines, and avoiding tight hairstyles can reduce stress on hair follicles. Consulting a dermatologist or trichologist early can help identify the cause and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Lifestyle Tips for Hair Health
Beyond medical treatments, adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in preventing hair loss. A balanced diet rich in vitamins like B12, D, and E, as well as minerals like zinc and iron, supports hair follicle health. Regular exercise improves blood circulation to the scalp, promoting hair growth. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can reduce cortisol levels, which may contribute to hair shedding in both men and women.
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is also crucial, as these habits can impair blood flow and nutrient delivery to hair follicles. For women, minimizing heat styling and chemical treatments can prevent damage to already fragile hair. By combining these lifestyle changes with medical interventions, individuals can maximize their chances of maintaining healthy, vibrant hair.
Comment / Reply From
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!